Description
Tas is a potential retrovirus described in the genome of the "giant intestinal roundworm" Ascaris lumbricoides (Aeby et al. 1986). Tas is the first retrovirus-like element found in any nematode species and received its name standing for transposon-like element of Ascaris (Aeby et al. 1986). Two variant forms present in the germ line - Tas-1 (the most abundant) and Tas-2 - have been characterized and approximately 50 copies are dispersed over about of 20 different chromosomal sites (Aeby et al. 1986). Tas gives the name and belongs to Tas clade (Copeland et al. 2005) within Branch 1 of the Bel/Pao family (Llorens et al. 2009).
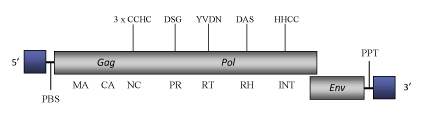
The genome of Tas is 7.6 Kb in size (7627 bp in length), including LTRs of respectively 256 (5’LTR) and 250 nts (3’LTR). The internal region of this element contains a Primer Binding Site (PBS), complementary to a tRNAArg, a coding region and a Polypurine Tract (PPT) upstream of the 3´LTR (Aeby et al. 1986; Felder et al. 1994). Although the coding region is disrupted by several stop codons and frameshiftings, the distinct gag and pol domains typical of LTR retrotransposons are clearly evident. In the Tas genome has also been identified an env-like gene located adjacent to the 3' LTR (Felder et al. 1994).
Structure
Figure not to scale. If present, long terminal repeats (LTRs) have been highlighted in blue. Amino acid motifs noted with lines indicate the conserved residues in each protein domain, abbreviations below mean:
| MA=matrix
|
PR=protease
|
DU or DUT=dUTPase
|
TM=transmembrane
|
TAV or IBMP=transactivator/viroplasmin or inclusion body matrix protein
|
| CA=capsid
|
RT=reverse transcriptase
|
INT=Integrase
|
CHR=chromodomain
|
| NC=nucleocapsid
|
RH=RNaseH
|
SU=surface
|
MOV=movement protein
|
| PPT=polypurine tract
|
PBS=primer binding site
|
ATF=aphid transmission factor
|
VAP=virion associated protein
|
Related literature
|
|