Element:HFV
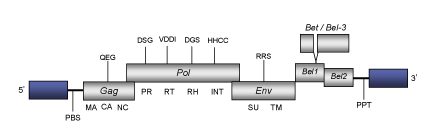
DescriptionHuman Foamy Virus (HFV) is a foamy retrovirus originally isolated from a nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient (Achong et al. 1971). Within the Retroviridae family, HFV belongs to the genus Spumaretrovirus (for a review see Meiering and Linial 2001). HFV has been isolated from patients with various diseases such as toxic encephalopathy (Cameron, Mirchall and Moses 1978), chronic myeloid leukemia (Young, Samuels and Clarke 1973), thyroiditis (Stancek et al. 1975; Werner and Gelderblom 1979; Wick et al. 1992) and Grave's disease (Ciampolillo et al. 1989). The pathology of HFV is however, not well known. The genomic structure of HFV is 13.2 Kb in size including LTRs of 1.8Kb. The internal region of this retrovirus displays a Primer Binding Site (PBS) complementary to a tRNALys1-2, Open Reading Frames (ORFs) for gag, pol and env genes characteristic of retroviruses, accessory bel1 and bel2 genes, and a Polypurine Tract (PPT) adjacent to the 3´LTR (Flügel 1991; Kogel, Aboud and Flügel 1995). As described by Muranyi and Flügel (1991) in human Spumaretrovirus, a chimeric protein termed Bet (or bel3) has also been observed in HFV; it derives from splicing of the N-terminal amino acids of bel1 in frame with the bulk of the bel2. Structure
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||