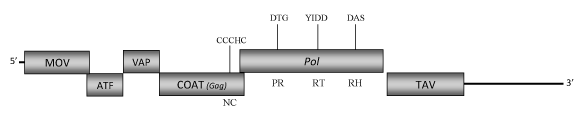
Element:EVCV
DescriptionEupatorium vein clearing virus (EVCV) is a plant pararetrovirus found in Eupatorium ornamental plants species, a genus of herbaceous perennial plants belonging to Asteraceae family, which was proposed to be a putative Caulimovirus-like member (Zhang et al. 2008, unpublished) of the Caulimoviridae family (International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses -ICTV- Fauquet et al. 2005). This is a perspective clearly supported by phylogenetic analyses inferred based on the COAT(GAG) and pol protein domains (Llorens et al 2009). EVCV virions are composed of a genomic circular double-stranded DNA (8463 bp long) encoding for six Open reading frames (ORFs) whose size and organization are similar to those of known caulimoviruses (Zhang et al. 2008, unpublished). The aminoacids sequences of the potentially predicted protein products show similarities to those encoded by the corresponding ORFs of known Caulimoviruses. ORF I encodes the putative movement protein (MOV), ORF II and ORF III are similar to the "aphid transmission factor" (ATF) and "virion associated protein" (VAP), respectively. ORF IV encodes the putative COAT protein and contains the "RNA-binding" motif characteristic of the Caulimoviridae COAT (Gag-like) domain (C-X-C-X2-C-X4-H-X4-C ) (Bouhida et al. 1993;Hull 1996; Llorens et al 2009). ORF V product is a polyprotein displaying the typical Pol domains -aspartic protease (PR), reverse transcriptase (RT) and RNase H (RH) – and ORF VI encodes a putative "Translational transactivator protein" (TAV) (Zhang et al. 2008, unpublished). A short intergenic region is present between ORFs V (Pol) and VI (TAV) as observed in the genome of other Caulimovirus-like species such as LLDAV. A second larger intergenic region is downstream to the ORF VI. In both cases the regions are rich in several stop codons. StructureFigure not to scale. If present, long terminal repeats (LTRs) have been highlighted in blue. Amino acid motifs noted with lines indicate the conserved residues in each protein domain, abbreviations below mean:
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||