Element:Ty3-1
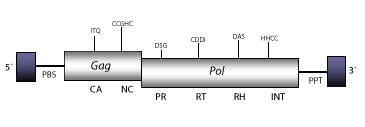
DescriptionTy3 is a LTR retrotransposon with specificity for integrating next to tRNA genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Clark et al. 1988; Hansen, Chalker, and Sandmeyer 1988; Hansen and Sandmeyer 1990). Ty3 does not bear a detectable chromodomain at the integrase domain, but is phylogenetically related to the Chromoviridae branch (Marín and Lloréns 2000), term suggested (Marín and Lloréns 2000) to describe the Ty3/Gypsy elements bearing chromodomain-integrases (Malik and Eickbush 1999). The chromovirus branch has been disclosed to be the most ancient phylogenetic pattern of Ty3/Gypsy retroelements (Gorinsek, Gubensek and Kordis 2004; 2005; Kordis 2005). Ty3 has at least two subtypes Ty3-1 and Ty3-2 (Hansen, Chalker, and Sandmeyer 1988). Ty3-1 has been taken as representative. Ty3-1 occurs, 16 bp upstream of the 5' end of a tRNACys gene, and its genomic structure is 5.5 Kb in size, including LTRs of 339 nt. The internal region of this element displays a Primer Binding Site (PBS), two Open Reading Frames (ORFs) for gag, and pol genes, and a Polypurine Tract (PPT) adjacent to the 3´LTR. The gag gene only encodes two major structural proteins, capsid (CA) and nucleocapsid (NC) (Hansen et al. 1992). Ty3 differs from other fungi and vertebrate chromoviruses in that it displays, like plant chromoviruses, a primer binding site (PBS) complementary to a tRNAi-Met. Note that the PBS of fungi and vertebrate chromoviruses, differs significantly from that used by plant chromoviruses. While plant chromoviruses use a methionine starting tRNA (iMet), fungi and vertebrate chromoviruses use their own self-priming mechanism to start the reverse transcription (Levin 1995 ; Butler et al. 2001). Structure
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||