Description
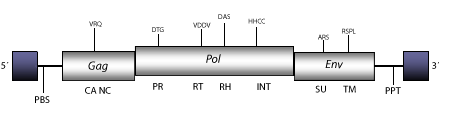
Gypsy is a fly-retrovirus originally described as a fragment of DNA cloned from several stocks of D. melanogaster, carrying suppressible mutations in the bithorax complex (Modolell, Bender, and Messelson 1983). Gypsy was the first retrovirus reported whose infectious properties were empirically tested in insects (Song et al. 1994; Kim et al. 1994) and has been also involved in occasional horizontal transfer events among other Drosophila species (Mizrokhi and Mazo 1991; Alberola and de Frutos 1996; Terzian et al. 2000). Gypsy belongs to the genus Errantiviridae (Boeke et al. 1999; Pringle 1998; 1999; Hull 1999), a lineage of fly-retroviruses and LTR retrotransposons phylogenetically related to 412/mdg1 clade (Tubio, Naveira and Costas 2005). The genomic structure of Gypsy is 7.4 Kb in size including LTRs of 482 nt. The internal region displays a Primer Binding Site (PBS) complementary to a tRNALys, three Open Reading Frames (ORFs) for gag, pol, and env genes, and a Polypurine Tract (PPT) adjacent to the 3´LTR (Marlor, Parkhurst y Corces 1986). Gypsy also displays an insulator element (gypsy insulator) of 350 nt at an untranslated zone of the transcribed 5´region (Smith and Corces 1992; Gdula, Gerasimova and Corces 1996; Gdula and Corces 1997). Insulators may normally function to compartmentalize the genome into independent domains of gene expression. Insulators can block activation of transcription when located between the enhancer and the promoter, and can shield transgenes from position effects caused by surrounding chromatin (Capelson and Corces 2004; Felsenfeld et al. 2004). The expression of Gypsy is repressed by a host gene named flamenco (Bucheton 1995 and references therein).
Structure
Figure not to scale. If present, long terminal repeats (LTRs) have been highlighted in blue. Amino acid motifs noted with lines indicate the conserved residues in each protein domain, abbreviations below mean:
| MA=matrix
|
PR=protease
|
DU or DUT=dUTPase
|
TM=transmembrane
|
TAV or IBMP=transactivator/viroplasmin or inclusion body matrix protein
|
| CA=capsid
|
RT=reverse transcriptase
|
INT=Integrase
|
CHR=chromodomain
|
| NC=nucleocapsid
|
RH=RNaseH
|
SU=surface
|
MOV=movement protein
|
| PPT=polypurine tract
|
PBS=primer binding site
|
ATF=aphid transmission factor
|
VAP=virion associated protein
|
Related literature
|
|