GINO
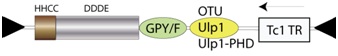
GINO is a recently described pool of exon-intron transposons (Marin 2010), which encode for a transposase (TR) showing the occurrence of a GPY/F module (Malik & Eickbush 1999) thought to mediate multimerization (Ebina et al. 2008) at its C-terminus. GINO elements show two additional modules adjacent to the GPY/F module. Depending on the element, the first may be an ovarian tumor (OTU) cysteine protease domain, or an Ulp1 protease catalytic domain (Marin 2010), the latter may also be coupled with a plant homeodomain (PHD) finger motif (according to Marin 2010). The second is in reverse frame and encodes for a Tc1 TR (Marin 2010). Full-length GINO elements are approximately 6.6 kb, and are flanked by terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) of approximately 45 nucleotides long (Marin 2010) (Figure not to scale). For simplicity´s sake the figure below shows the genomic structure without introns.
GINO elements belong to the phylogenetic cluster of TRs and integrases (INTs) constituted by the GINGER1-like transposons (Bao et al. 2010) (which give the name to the cluster), the two GIN-like host genes of vertebrates (Llorens & Marin 2001; Bao et al. 2010; Marin 2010), and other transposons called GINA and GINNY (Marin 2010). There are two complementary classifications for the GINGER1 elements. Based on sequence, these elements can be classified as DDE TRs and INTs. Based on INT-like structural potential similarities, the INT coded by GINGER1 elements are members of the Retroviral Integrase Superfamily (Nowotny 2009) of nucleic acid-processing enzymes involved in: a) selfish evolution; b) replication and repair of DNA; c) recombination and gene fusion; d) RNA-mediated gene silencing; and e) oncogenesis.
