Difference between revisions of "Element:ComYMV"
imported>Gydbwiki |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 12:44, 22 March 2010
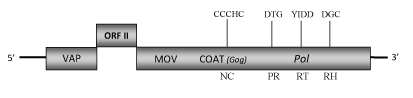
DescriptionCommelina yellow mottle virus (ComYMV or CoYMV) is a pararetrovirus infecting the monocot weed Commelina diffusa, a species of perennial or annual herbaceous plants commonly called "dayflowers" belonging to Commelina genus (Migliori and Lastra 1978; Medberry et al. 1990). ComYMV represents the type member for the genus Badnavirus of Caulimoviridae family (International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses -ICTV- Fauquet et al. 2005) and according to Llorens et al. 2009 it is located within Class 2 of the Caulimoviridae family. ComYMV has non-enveloped bacilliform particles of 133 x 24 nm containing a circular dsDNA of about 7.4 Kb in size (7489 bp long) (Lockhart 1990; Medberry et al. 1990). Although had been identified five putative open reading frames (ORFs) -three of these located on the plus-strand of the genome (ORFs I, II, III) and other two on the minus-strand (designated x and y and encoding proteins larger than 10 kDa)- it is likely that only the three ORFs of the plus-strand are expressed (Medberry et al. 1990). The functions of the putative ORF I and ORF II products (200 and 135 amino acids (aa) long, respectively) have not been well described yet. However has been demonstrated that the protein potentially encoded by ORF I is associated to the virion (VAP) and probably it plays a role in virion maturation (Cheng et al. 1996). The smallest ORF II protein has been localized to the external surface of the virion and it has been suggested its association with both mature and immature virions (Cheng et al. 1996). The polyprotein encoded by ORF III contains the typical Badnavirus cell-to-cell movement protein (MOV) (Cheng et al. 1998), viral coat protein (COAT), aspartic protease (PR), reverse transcriptase (RT) and RNase H (RH) domains (Medberry et al. 1990; Tzafrir et al. 1997). It includes a "RNA-binding" motif sequence "C-X-C-X2-C-X4-H-X4-C" and a second large cysteine-rich region "C-X2-C-X11-C-X2-C-X4-C-X2-C" (only observed in Badna- and Tungroviruses) located at the C-terminus of the COAT (gag)-like region and similar to those identified in the nucleocapsid domains of LTR retroelements (Llorens et al. 2009). Mealybugs are the natural vectors for ComYMV, but the virus can also be transmitted both mechanically and by Agroinoculation (Lockhart 1990; Medberry et al. 1990; Cheng et al. 1996; Tzafrir et al. 1997). Structure
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||