Difference between revisions of "Element:Sushi-ichi"
imported>Gydbwiki |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 16:04, 11 November 2009
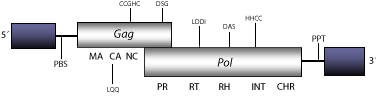
DescriptionSushi-ichi is a LTR retrotransposon characterized in Takifugu rubripes (Poulter and Butler 1998; Butler et al. 2001; Volff et al. 2003). Sushi belongs to V-clade (Llorens et al. 2009) the chromovirus lineage of vertebrate-like Ty3/Gypsy LTR retrotransposons (Marín and Lloréns 2000) characterized by encoding for chromodomain-integrases (Malik and Eickbush 1999). The chromovirus branch has been disclosed to be the most ancient phylogenetic pattern of Ty3/Gypsy retroelements (Gorinsek, Gubensek and Kordis 2004; 2005; Kordis 2005). Sushi has several subtypes. Sushi-ichi is taken as representative. Its genome is 5.6 Kb in size, including LTRs of 560 nt. The internal region of this element displays a Primer Binding Site (PBS), two Open Reading Frames (ORFs) for gag, and pol genes, and a Polypurine Tract (PPT) adjacent to the 3´LTR (Poulter and Butler 1998; Butler et al. 2001; Volff et al. 2003). This element presents a detectable chromodomain at the C-terminal end of the integrase pol polyprotein domain. The PBS of fungi and vertebrate chromoviruses, differs significantly from that used by plant chromoviruses. While plant chromoviruses use a methionine starting tRNA (iMet), fungi and vertebrate chromoviruses use their own self-priming mechanism to start the reverse transcription (Levin 1995 ; Butler et al. 2001). Structure
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||