Element:TSI-9
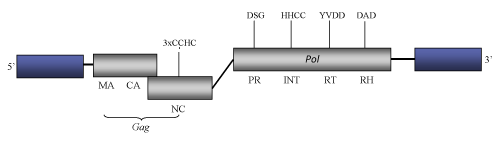
DescriptionTSI-9 is one of the several transposable elements described in the genome of the foxtail millet (Setaria italica ssp.) (Kawase et al. 2005). TSI-9 belongs to the SIRE clade of Ty1/Copia plant LTR retrotransposons and potential retroviruses (Fauquet et al. 2005). This clade is evolutionarily related to another clade of plant Ty1/Copia LTR retrotransposons called Oryco (Llorens et al. 2009). SIRE clade gives the name to a genus within the current ICTV classification of the Ty1/Copia into three genera – Pseudovirus, Hemivirus and Sirevirus (Boeke et al. 2005). The full-lenght genome of TSI-9 is 9331 bp long and includes two 1238-bps LTRs flanking an internal coding region that contains three Open Reading Frames (ORFs). The internal region displays the characteristic gag and pol domains (Kawase et al. 2005) but does not show any env-like domain. In comparison to other Ty1/Copia elements, a taxonomically relevant feature specific of Sire-like elements is their extremely large gag C-terminus consistent with the NC domain, which may display two or three CCHC arrays (Llorens et al. 2009) Structure
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||