Element:Cereba
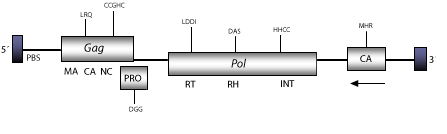
DescriptionCereba is a LTR retrotransposon characterized in the centromeres of Hordeum vulgare (Presting et al. 1998). This element belongs to the Chromoviridae branch, term suggested (Marín and Lloréns 2000) to describe the Ty3/Gypsy elements bearing chromodomain-integrases (Malik and Eickbush 1999). The chromovirus branch is probably the most ancient phylogenetic pattern of Ty3/Gypsy retroelements (Gorinsek, Gubensek and Kordis 2004; 2005; Kordis 2005). Within chromoviruses, Cereba belongs to CRM clade; a centromere-associated sub-lineage characterized by encoding integrases, clearly divergent from that encoded by other lineages of chromoviruses (Gorinsek, Gubensek and Kordis 2004). The genomic structure of Cereba is 11.6 Kb in size, including putative LTRs of 153 nt. The internal region displays a Primer Binding site (PBS), and three Open Reading Frames (ORFs) for gag, pro, and pol genes (Presting et al. 1998). The sequence analyzed by us also displays upstream to the 3´LTR, a putative ORF in reverse frame (-3) (nt 10023-9067), which codifies for a putative 319 aa extra capsid (CA) domain. The PBS of fungi and vertebrate chromoviruses, differs significantly from that used by plant chromoviruses. While plant chromoviruses use a methionine starting tRNA (iMet), fungi and vertebrate chromoviruses use their own self-priming mechanism to start the reverse transcription (Levin 1995 ; Butler et al. 2001). Structure
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||