Element:JSRV
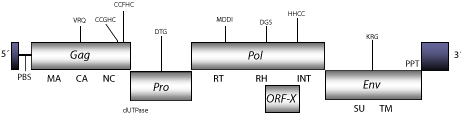
DescriptionJaagsiekte Sheep Retrovirus (JSRV) is a retrovirus originally reported in sheep and cattle, and is the causal agent of infectious pulmonary adenomatosis (Dungal, Gislason, and Taylor 1938; Coetzee, Els and Verwoerd 1976; Verwoerd et al. 1983; Demartini et al. 1987; Tustin et al. 1988; York et al. 1991; 1992). JSRV has also been reported in the mononuclear phagocytes and lymphocytes C and T of sheep (Holland et al. 1999). The genetic organization of this retrovirus is characteristic of type-B oncoviruses (York et al. 1992). Thus, this retrovirus belongs to the genus Betaretrovirus, which comprises both B- and D-type retroviruses. Interestingly, D-type betaretroviruses present a common surface receptor also used by the baboon and cat endogenous C-type gammaretroviruses (BaEVM, RD114), cellular infection by any of them can interfere with other D-type members, and also with BaEVM and RD114 (Chatterjee and Hunter 1980; Sommerfelt and Weiss 1990 ). This evidence seems to be related with the high similarity displayed between env polyproteins encoded by gammaretroviruses and D-type betaretroviruses, indicating that betaretroviruses and gammaretroviruses may have been involved in an ancient recombinatorial event (Sonigo et al 1986; Fauquet et al. 2005) or that they share a common ancestor (see env tree in section "phylogenies"). The genomic structure of JSRV is 7.5 Kb in size including pro-5´LTR of 126 nt and pro-3´LTR of 277 nt. The internal region of this retrovirus displays a Primer Binding Site (PBS) complementary to a tRNALys1,2, five Open Reading Frames (ORFs) for gag, dut/pro, pol, Orf-x, and env genes, and a Polypurine Tract (PPT) adjacent to the 3´ LTR (York et al. 1991; 1992; Bai et al. 1999; Elder et al. 1992; Payne and Elder 2001). Structure
Related literature |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||